Climate Change Impact on US Coasts: Adaptation & Mitigation Strategies
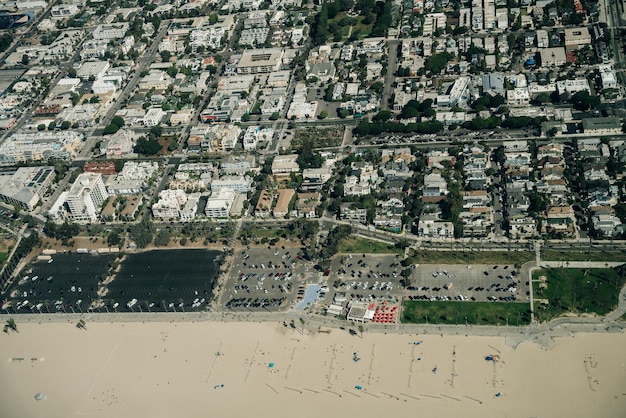

The impact of climate change on US coastal communities involves accelerating sea-level rise, increased storm intensity, and ecosystem disruption, necessitating innovative adaptation strategies and mitigation efforts to protect vulnerable populations and natural resources.
The relentless march of climate change is no longer a distant threat; it’s a present-day reality for many US coastal communities. The confluence of rising sea levels, increasingly ferocious storms, and the degradation of vital coastal ecosystems is reshaping the very fabric of these communities. Understanding the impact of climate change on US coastal communities, along with the latest adaptation strategies and mitigation efforts, is critical for building a more resilient future.
Understanding the Coastal Climate Crisis in the US
The United States boasts more than 95,000 miles of coastline, a dynamic and ecologically diverse region that supports a significant portion of the nation’s population and economy. However, these coastal areas are increasingly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including rising sea levels, more intense storms, and coastal erosion. The intricate interplay of these factors poses significant challenges to the sustainability and well-being of coastal communities.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of the coastal climate crisis is paramount. The problem goes beyond merely rising sea levels; it involves a complex web of interconnected issues that amplify the threat to coastal regions. Identifying these elements is crucial for devising effective, targeted responses.
Key Climate Change Impacts on US Coasts
Several key impacts of climate change are already reshaping US coastlines, underscoring the urgency for robust mitigation and adaptation measures.
- Sea-Level Rise: Driven by thermal expansion of seawater and melting glaciers and ice sheets, sea-level rise threatens to inundate low-lying areas, erode coastlines, and increase the frequency of coastal flooding.
- Increased Storm Intensity: Warmer ocean temperatures fuel more powerful hurricanes and nor’easters, leading to devastating storm surges, damaging winds, and heavy rainfall.
- Coastal Erosion: Rising sea levels and increased storminess exacerbate coastal erosion, threatening infrastructure, property, and natural habitats.
- Ocean Acidification: The absorption of excess atmospheric carbon dioxide by the ocean leads to ocean acidification, which harms marine life, particularly shellfish and coral reefs.
These impacts are not isolated events; they are interconnected and reinforce each other, creating a cascade of challenges for coastal communities. For instance, sea-level rise increases the vulnerability of coastal areas to storm surges, while ocean acidification weakens coral reefs, which provide natural coastal protection.
In conclusion, the coastal climate crisis in the US is a complex and multifaceted challenge that requires a comprehensive understanding of its key drivers and impacts. Recognizing the interconnectedness of these factors is essential for developing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies that can safeguard the future of US coastal communities.
Latest Adaptation Strategies for Coastal Resilience
As the impacts of climate change intensify, coastal communities are increasingly turning to a range of adaptation strategies to enhance resilience and protect lives, property, and ecosystems. These strategies involve a combination of structural, natural, and policy-based approaches aimed at reducing vulnerability and building long-term adaptive capacity. Exploring the most recent adaptation strategies allows us to grasp the comprehensive efforts underway to fortify these coastal regions.
Coastal adaptation is not a one-size-fits-all solution; it requires a tailored approach that considers the specific characteristics of each community, including its geography, demographics, and economic activities.
Innovative Approaches to Coastal Adaptation
Several innovative approaches are gaining traction in coastal communities, offering promising solutions to the challenges posed by climate change.
- Living Shorelines: Utilizing natural elements such as oyster reefs, salt marshes, and vegetation to stabilize shorelines, reduce erosion, and provide habitat for marine life.
- Elevating Structures: Raising homes and other buildings above projected flood levels to minimize damage from storm surges and sea-level rise.
- Managed Retreat: Strategically relocating communities away from vulnerable coastal areas to higher ground, allowing for the restoration of natural coastal habitats.
These strategies are not mutually exclusive; in fact, they are often most effective when implemented in combination. For example, a community might combine living shorelines with elevated structures to provide both natural and structural protection against coastal hazards.
Living shorelines, in particular, offer a compelling alternative to traditional hard infrastructure such as seawalls, which can disrupt natural coastal processes and harm marine ecosystems. By mimicking natural coastal features, living shorelines can provide multiple benefits, including erosion control, habitat creation, and improved water quality.

In summary, the latest adaptation strategies for coastal resilience encompass a diverse range of approaches that aim to reduce vulnerability, protect coastal resources, and enhance the long-term adaptive capacity of coastal communities. These strategies require a collaborative effort involving governments, scientists, engineers, and community members to ensure their effective implementation and sustainability.
State and Federal Mitigation Efforts to Curb Climate Change
Mitigation refers to actions taken to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, the primary driver of climate change. While adaptation focuses on coping with the impacts of climate change, mitigation aims to address the root cause of the problem by reducing the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Investigating the state and federal mitigation efforts is critical to understanding the full scope of actions intended to curb climate change and shield vulnerable coastal communities.
Both state and federal governments have a crucial role to play in implementing effective mitigation policies and initiatives. These efforts often involve a combination of regulatory measures, incentives, and investments in clean energy technologies.
Key Mitigation Policies and Initiatives
A variety of policies and initiatives have been implemented at both the state and federal levels to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote a transition to a low-carbon economy.
- Renewable Energy Standards: Requiring utilities to generate a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources such as solar, wind, and geothermal.
- Carbon Pricing Mechanisms: Implementing carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems to put a price on carbon emissions, incentivizing businesses and individuals to reduce their carbon footprint.
- Energy Efficiency Programs: Promoting energy efficiency through building codes, appliance standards, and incentives for energy-efficient upgrades.
The Inflation Reduction Act and Climate Mitigation
The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 represents a significant federal investment in climate mitigation, with billions of dollars allocated to clean energy tax credits, grants, and loan programs. This legislation aims to accelerate the deployment of renewable energy technologies, promote energy efficiency, and support the development of a clean energy economy.
Many states have also established their own climate goals and implemented policies to achieve these goals. California, for example, has set a goal to achieve carbon neutrality by 2045 and has implemented a comprehensive set of climate policies, including a cap-and-trade program and ambitious renewable energy standards.
Ultimately, effective mitigation requires a concerted effort at all levels of government, as well as engagement from businesses, communities, and individuals. By working together to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, we can protect coastal communities and ecosystems from the worst impacts of climate change.
The Role of Community Engagement in Climate Action
Climate change is not only an environmental issue; it is also a social and economic issue that affects communities in profound ways. Therefore, successful climate action requires the active engagement of communities in the decision-making process. Assessing the role of community engagement in climate action is essential for creating effective, inclusive, and sustainable solutions.
Community engagement involves empowering residents to participate in planning, implementing, and monitoring climate change initiatives. This can take many forms, from public meetings and workshops to citizen science projects and community-based adaptation planning.
Strategies for Effective Community Engagement
Several strategies can help foster effective community engagement in climate action:
- Building Trust: Establishing open and transparent communication channels between government agencies, scientists, and community members.
- Providing Education and Resources: Equipping residents with the knowledge and tools they need to understand climate change and take action.
- Creating Opportunities for Participation: Offering diverse opportunities for residents to participate in climate change initiatives, from volunteering to providing feedback on proposed policies.
Community engagement can also help ensure that climate change initiatives are equitable and just, addressing the needs of vulnerable populations and promoting a fair distribution of benefits and burdens. For example, community-based adaptation planning can help identify and address the specific vulnerabilities of low-income communities to climate change impacts.
Moreover, community engagement can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility for climate action, leading to greater support for policies and initiatives. When residents feel that their voices are heard and their concerns are addressed, they are more likely to support and participate in climate change efforts.
In conclusion, the role of community engagement in climate action is paramount. By fostering collaboration, building trust, and empowering residents to participate in decision-making processes, we can create more effective, inclusive, and sustainable climate solutions that benefit all members of society.
Economic Considerations for Coastal Climate Resilience
Addressing the impacts of climate change on US coastal communities requires not only environmental and social considerations but also careful attention to economic factors. Evaluating the economic considerations for coastal climate resilience helps in justifying investments in adaptation and mitigation efforts, as well as identifying economic opportunities associated with a transition to a climate-resilient economy.
The economic impacts of climate change on coastal communities can be substantial, including:
- Property Damage: Rising sea levels, increased storm intensity, and coastal erosion can cause significant damage to homes, businesses, and infrastructure.
- Loss of Tourism Revenue: Damage to beaches, coral reefs, and other coastal attractions can reduce tourism revenue, impacting local economies.
- Increased Insurance Costs: Insurers may raise premiums or withdraw coverage in vulnerable coastal areas, making it more difficult for residents and businesses to afford insurance.
However, investing in coastal climate resilience can also generate economic benefits, including:
Investing in coastal climate resilience not only protects coastal communities from the impacts of climate change but also creates jobs, stimulates economic growth, and enhances the long-term sustainability of coastal economies.
Future Outlook: Challenges and Opportunities
Looking ahead, US coastal communities face both significant challenges and exciting opportunities as they grapple with the impacts of climate change. Understanding these challenges and opportunities is essential for charting a course toward a more resilient and sustainable future.
One of the key challenges is the uncertainty surrounding the magnitude and timing of future climate change impacts. While climate models provide valuable projections, there is still uncertainty about the exact rate of sea-level rise, the frequency and intensity of storms, and the extent of coastal erosion.
Another challenge is the financial cost of adaptation and mitigation. Implementing effective climate change strategies requires significant investments in infrastructure, technology, and community engagement. Securing adequate funding for these efforts can be a major hurdle, particularly for communities with limited resources.
Despite these challenges, there are also many opportunities to build a more resilient and sustainable future for US coastal communities. These opportunities include:
- Technological Innovation: Developing and deploying innovative technologies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, enhance coastal protection, and improve climate resilience.
- Sustainable Economic Development: Promoting sustainable economic development strategies that create jobs, protect the environment, and enhance community well-being.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Forging strong partnerships between governments, businesses, communities, and research institutions to leverage resources, share knowledge, and accelerate climate action.
In conclusion, the future outlook for US coastal communities is one of both challenges and opportunities. By embracing innovation, promoting sustainable development, and fostering collaboration, we can build a more resilient and sustainable future for these vulnerable regions.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🌊 Sea-Level Rise | Driven by melting ice and thermal expansion, it threatens coastal inundation. |
| ⛈️ Storm Intensity | Warmer waters fuel more intense hurricanes and coastal storms, increasing damage. |
| 🌿 Living Shorelines | Natural erosion control using oyster reefs, marshes, and vegetation. |
| 💰 Economic Impacts | Property damage, tourism loss, and rising insurance costs challenge coastal economies. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
The primary threats include rising sea levels, increased intensity of storms, coastal erosion, and ocean acidification. These factors combine to endanger infrastructure, natural habitats, and the overall stability of coastal economies.
▼
A living shoreline is a natural approach to coastal protection using elements like oyster reefs and salt marshes. It helps stabilize shorelines, reduce erosion, provide habitat, and improve water quality, offering a sustainable alternative to hard infrastructure.
▼
The Inflation Reduction Act invests billions in clean energy tax credits, grants, and loan programs. This accelerates the deployment of renewable energy, promoting energy efficiency, and supporting a transition to a clean energy economy.
▼
Community engagement empowers residents to participate in climate initiatives. It builds trust, provides education, and ensures climate action is equitable, addressing the needs of all, especially vulnerable populations, and fosters a sense of shared responsibility.
▼
Economic impacts include property damage due to storms and sea-level rise, loss of tourism revenue from damaged attractions, and increased insurance costs. These factors threaten economic stability in coastal communities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the impact of climate change on US coastal communities represents a complex and urgent challenge. By embracing innovative adaptation strategies, committing to strong mitigation efforts, engaging communities in climate action, and carefully considering the economic consequences, we can work towards a more resilient and sustainable future for these vulnerable regions. The path forward requires a concerted effort from governments, businesses, and individuals alike, all working together to protect our precious coastlines for generations to come.





