IPCC Report: Rising Sea Levels & Impact on US Coastal Communities
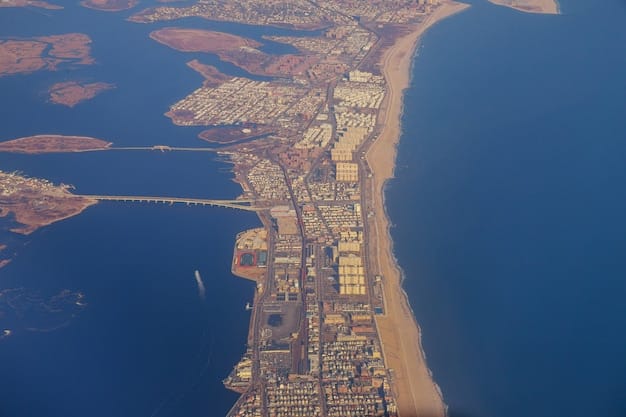

The latest IPCC report warns of accelerating sea-level rise, threatening US coastal communities with increased flooding, erosion, and displacement, demanding urgent adaptation and mitigation strategies.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has released its latest report, painting a stark picture of our planet’s future. A key focus of the report is the accelerating rise in sea levels and the profound impact this will have on coastal communities, particularly in the US. Let’s delve into the details of **what the latest IPCC report says about rising sea levels and their impact on US coastal communities**.
Understanding the IPCC and Sea Level Projections
The IPCC, a leading international body for assessing climate change, synthesizes the work of thousands of scientists worldwide. Its reports provide comprehensive assessments of climate change science, impacts, and potential response options. Understanding their projections for sea level rise is crucial for preparing for the future.
The IPCC uses a range of scenarios to project future sea levels, considering different levels of greenhouse gas emissions. These scenarios help policymakers and communities understand the potential range of impacts and plan accordingly.
Key Projections from the Latest IPCC Report
The latest report builds upon previous assessments, incorporating new data and improved modeling techniques. Here are some of the key projections:
- Even under the most optimistic emission scenarios, sea levels will continue to rise throughout the 21st century.
- The rate of sea level rise is accelerating, meaning that future increases will be more rapid than those observed in the past.
- Higher emission scenarios lead to significantly greater sea level rise, with potentially catastrophic consequences for coastal regions.
- The report emphasizes that committed sea level rise, meaning the rise that is already locked in due to past emissions, will continue for centuries, even if emissions are drastically reduced.
These projections highlight the urgency of addressing climate change and the need for proactive adaptation measures in coastal communities. Ignoring the warnings in the IPCC report will lead to devastating consequences.
Impacts of Rising Sea Levels on US Coastal Communities
Rising sea levels pose a complex threat to coastal communities, impacting infrastructure, ecosystems, and economies. These impacts are not uniform, with some regions being more vulnerable than others.
The eastern seaboard, the Gulf Coast, and low-lying island communities are particularly at risk. Understanding the specific impacts in these areas is crucial for effective adaptation planning.
Specific Threats Faced by Coastal Communities
Here are some of the specific threats posed by rising sea levels:
- Increased flooding: Coastal flooding events are becoming more frequent and severe, inundating homes, businesses, and infrastructure.
- Erosion: Rising sea levels erode shorelines, leading to loss of land and damage to coastal ecosystems.
- Saltwater intrusion: Saltwater can contaminate freshwater sources, impacting drinking water supplies and agriculture.
- Loss of wetlands: Coastal wetlands, which provide important ecosystem services such as storm protection and habitat for wildlife, are being lost to rising sea levels.
These threats are not isolated events; they often interact and compound each other. For example, increased flooding can exacerbate erosion, leading to further land loss and infrastructure damage.
Economic Consequences of Sea Level Rise
The economic consequences of rising sea levels are substantial, impacting various sectors and industries. These impacts extend beyond direct damage to coastal properties.
The costs of inaction far outweigh the investments needed for adaptation. Understanding these economic consequences is essential for justifying investments in preventative measures.
Economic Sectors at Risk
Several economic sectors are particularly vulnerable to the impacts of rising sea levels:
- Tourism: Coastal tourism is a major industry in many states. Rising sea levels can damage beaches, coastal attractions, and infrastructure, leading to decreased tourism revenue.
- Fisheries: Coastal fisheries are threatened by habitat loss and changes in water salinity.
- Real estate: Coastal properties are losing value as the risk of flooding and erosion increases.
- Shipping and transportation: Coastal ports and transportation infrastructure are vulnerable to flooding and storm surge.
These economic impacts are not limited to coastal areas. Disruptions to supply chains and increased insurance costs can ripple through the national economy.
Adaptation Strategies for Coastal Communities
Adaptation strategies are essential for mitigating the impacts of rising sea levels. These strategies involve a range of measures, from protecting existing infrastructure to relocating vulnerable communities.
Effective adaptation requires a collaborative effort involving governments, communities, and the private sector. Prioritizing adaptation planning now will reduce future costs and risks.
Types of Adaptation Strategies
Here are some common adaptation strategies:
- Building seawalls and levees: These structures can protect coastal areas from flooding and erosion.
- Restoring wetlands: Wetlands can act as natural buffers, absorbing storm surge and reducing erosion.
- Elevating buildings: Raising buildings above flood levels can protect them from damage.
- Managed retreat: Relocating communities away from vulnerable areas can avoid future damage.
The choice of adaptation strategy will depend on the specific context of the coastal community, including its geography, economy, and social values. A combination of strategies is often the most effective approach.

The Role of Mitigation in Addressing Sea Level Rise
While adaptation is crucial for managing the immediate impacts of rising sea levels, mitigation is essential for addressing the underlying cause: climate change. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is the only way to slow down and eventually stop sea level rise.
Mitigation efforts must be global in scale to be effective. The US plays a critical role in reducing its emissions and encouraging other countries to do the same.
Key Mitigation Measures
Here are some key mitigation measures:
- Transitioning to renewable energy sources: Replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydro power can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Improving energy efficiency: Reducing energy consumption through improved building design, transportation systems, and industrial processes can also lower emissions.
- Protecting and restoring forests: Forests absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to mitigate climate change.
These measures require significant investments and policy changes, but the long-term benefits far outweigh the costs. Failing to address climate change will lead to even greater economic and environmental damage.
Policy and Planning for a Future with Rising Seas
Effective policy and planning are essential for helping coastal communities adapt to and mitigate the impacts of rising sea levels. This requires coordination across all levels of government.
Policies should be based on the best available science and incorporate the long-term risks associated with sea level rise. Integrating climate change considerations into all aspects of coastal management will ensure a more resilient future.
Policy Priorities
Here are some policy priorities:
- Developing comprehensive coastal management plans: These plans should address the risks of sea level rise and outline adaptation strategies.
- Investing in research and development: Further research is needed to improve our understanding of sea level rise and develop more effective adaptation technologies.
- Providing funding for adaptation projects: Coastal communities need financial assistance to implement adaptation measures.
These policies require a long-term commitment and a willingness to make difficult choices. However, by taking action now, we can protect our coastal communities and ensure a sustainable future.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🌊 Accelerating Rise | Sea levels are rising at an increasing rate, posing a greater threat over time. |
| 🏘️ Coastal Impacts | US coastal communities face increased flooding, erosion, and saltwater intrusion. |
| 💰 Economic Risks | Tourism, fisheries, and real estate sectors are economically vulnerable to rising seas. |
| 🛡️Adaptation Needed | Adaptation strategies, like seawalls and wetland restoration, are crucial for protection. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
▼
The IPCC is the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. It’s the leading international body for assessing climate change related to human activity, its impacts and future risks, and options for adaptation and mitigation.
▼
Sea level rise projections vary depending on emission scenarios. The IPCC suggests that even under low emission scenarios, sea levels will continue to rise during the 21st century, with higher emission scenarios leading to substantially greater increases.
▼
The eastern seaboard, the Gulf Coast, and low-lying island communities are particularly vulnerable. These regions are susceptible to increased flooding, erosion, and saltwater intrusion due to rising sea levels.
▼
Adaptation strategies include building seawalls and levees, restoring wetlands, elevating buildings, and managed retreat (relocating communities away from vulnerable areas) as ways to protect and adapt to rising sea levels.
▼
Mitigation refers to efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, which is the primary driver of climate change and sea-level rise. It’s crucial because it addresses the root cause of the problem, slowing down and eventually stopping further sea level rise.
Conclusion
The latest IPCC report underscores the urgent need to address rising sea levels and their impact on US coastal communities. While adaptation measures are crucial for managing the immediate consequences, mitigation efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions are essential for long-term sustainability. Ignoring the report’s findings poses significant threats to coastal economies, ecosystems, and the well-being of millions of residents, emphasizing the need for proactive planning and decisive action.





